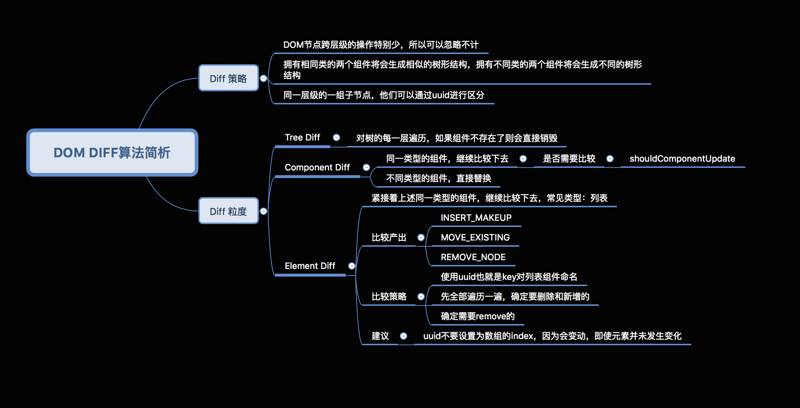
React15diff算法策略
React diff原理
传统diff算法通过循环递归对节点进行依次对比,效率低下,算法复杂度达到 O(n^3),其中 n 是树中节点的总数。
react却利用其特殊的diff算法做到了O(n^3)到O(n)的飞跃性的提升,而完成这一壮举的法宝就是下面这三条看似简单的diff策略:
- Web UI中DOM节点跨层级的移动操作特别少,可以忽略不计。(tree diff)
- 拥有相同类的两个组件将会生成相似的树形结构,拥有不同类的两个组件将会生成不同的树形结构。(component diff)
- 对于同一层级的一组子节点,它们可以通过唯一 id 进行区分。(element diff)
tree diff (同层比较,不同直接删)
基于策略一,React 对树的算法进行了简洁明了的优化,即对树进行分层比较,两棵树只会对同一层次的节点进行比较。
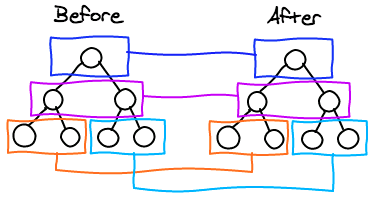
既然 DOM 节点跨层级的移动操作少到可以忽略不计,针对这一现象,React只会对相同层级的 DOM 节点进行比较,即同一个父节点下的所有子节点。当发现节点已经不存在时,则该节点及其子节点会被完全删除掉,不会用于进一步的比较。这样只需要对树进行一次遍历,便能完成整个 DOM 树的比较。
策略一的前提是Web UI中DOM节点跨层级的移动操作特别少,但还是有,由于 React 只会简单地考虑同层级节点的位置变换,而对于不 同层级的节点,只有创建和删除操作,所以如果是跨层级移动就是把之前的销毁,然后在重新创建,这非常消耗性能。
component diff (同类比较,不同直接删)
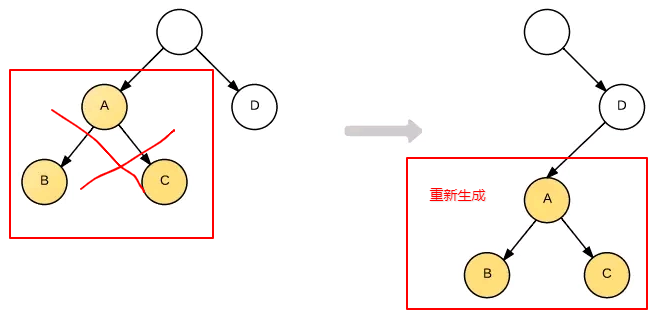
- 如果是同一类型的组件,按照原策略继续比较 Virtual DOM 树即可。
- 如果不是,则将该组件判断为 dirty component,从而替换整个组件下的所有子节点。
- 对于同一类型的组件,可通过props的浅比较shouldComponentUpdate()来判断是否变了。但是如果调用了forceUpdate方法,shouldComponentUpdate则失效。
element diff (加key判断是否需要删除)
当节点处于同一层级时,diff 提供了 3 种节点操作,分别为 INSERT_MARKUP (插入)、MOVE_EXISTING (移动)和 REMOVE_NODE (删除)。
- INSERT_MARKUP :新的组件类型不在旧集合里,即全新的节点,需要对新节点执行插入操作。
- MOVE_EXISTING :旧集合中有新组件类型,且 element 是可更新的类型,- generateComponentChildren 已调用receiveComponent ,这种情况下 - prevChild=nextChild ,就需要做移动操作,可以复用以前的 DOM 节点。
- REMOVE_NODE :旧组件类型,在新集合里也有,但对应的 element 不同则不能直接复用和更新,需要执行删除操作,或者旧组件不在新集合里的,也需要执行删除操作。
如果两颗树的同一层仅仅是位置不对,但diff的时候是对比的相同位置的节点,就会认为节点不同而选择删除并创建新的。
React针对这一现象提出了一种优化策略:允许开发者对同一层级的同组子节点,添加唯一 key 进行区分。
通过key可以准确地发现新旧集合中的节点都是相同的节点,因此无需进行节点删除和创建,只需要将旧集合中节点的位置进行移动,更新为新集合中节点的位置。
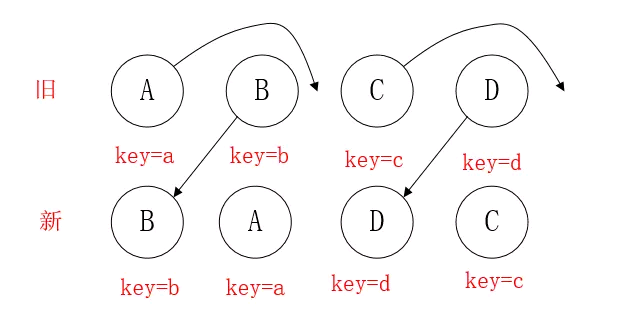
注意:在开发过程中,尽量减少类似将最后一个节点移动到列表首部的操作。当节点数量过大或更新操作过于频繁时,这在一定程度上会影响React的渲染性能。
ChildrenDiff的源码
通过key可以准确地发现新旧集合中的节点都是相同的节点,因此无需进行节点删除和创建,只需要将旧集合中节点的位置进行移动,更新为新集合中节点的位置 源码:
_updateChildren: function(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context) {
var prevChildren = this._renderedChildren;
var nextChildren = this._reconcilerUpdateChildren(
prevChildren, nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context
);
if (!nextChildren && !prevChildren) {
return;
}
var name;
var lastIndex = 0;
var nextIndex = 0;
// 首先对新集合的节点进行循环遍历
for (name in nextChildren) {
// 通过唯一 key 可以判断新老集合中是否存在相同的节点
if (!nextChildren.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
continue;
}
var prevChild = prevChildren && prevChildren[name];
var nextChild = nextChildren[name];
if (prevChild === nextChild) {
// 移动节点
this.moveChild(prevChild, nextIndex, lastIndex);
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex;
} else {
if (prevChild) {
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
// 删除节点
this._unmountChild(prevChild);
}
// 初始化并创建节点
this._mountChildAtIndex(
nextChild, nextIndex, transaction, context
);
}
nextIndex++;
}
for (name in prevChildren) {
if (prevChildren.hasOwnProperty(name) &&
!(nextChildren && nextChildren.hasOwnProperty(name))) {
this._unmountChild(prevChildren[name]);
}
}
this._renderedChildren = nextChildren;
},
// 移动节点
moveChild: function(child, toIndex, lastIndex) {
if (child._mountIndex < lastIndex) {
this.prepareToManageChildren();
enqueueMove(this, child._mountIndex, toIndex);
}
},
// 创建节点
createChild: function(child, mountImage) {
this.prepareToManageChildren();
enqueueInsertMarkup(this, mountImage, child._mountIndex);
},
// 删除节点
removeChild: function(child) {
this.prepareToManageChildren();
enqueueRemove(this, child._mountIndex);
},
_unmountChild: function(child) {
this.removeChild(child);
child._mountIndex = null;
},
_mountChildAtIndex: function(
child,
index,
transaction,
context) {
var mountImage = ReactReconciler.mountComponent(
child,
transaction,
this,
this._nativeContainerInfo,
context
);
child._mountIndex = index;
this.createChild(child, mountImage);
},
根据源码分析Key的比对策略
lastIndex表示访问过的新节点在老集合中最右的位置(即最大的位置)
- 如果新集合中当前访问的节点比 lastIndex 大,说明当前访问节点在老集合中就比上一个节点位置靠后,则该节点不会影响其他节点的位置,因此不用添加到差异队列中,即不执行移动操作
- 只有当访问的节点比 lastIndex 小时,才需要进行移动操作。
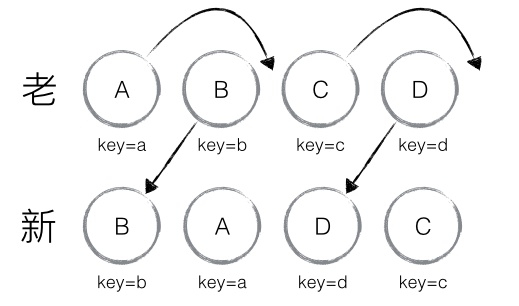
- 比如下图前面的AB怎么玩都不用触发CD的移动,你一眼就能看出来,但的告诉React才行,所以标记一个lastIndex来告诉React后面的需不需动
第一种没有删除的现象
| column0 | column1 | column2 | column3 | column4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nextIndex | 节点 | mountIndex | lastIndex | 操作 |
| 0 | B | 1 | 0 | mountIndex(1)>lastIndex(0),lastIndex=mountIndex |
| 1 | A | 0 | 1 | mountIndex(0) < lastIndex(1),节点A移动至index(1)的位置 |
| 2 | D | 3 | 1 | mountIndex(3)> lastIndex(1),lastIndex=mountIndex |
| 3 | C | 2 | 3 | mountIndex(2)< lastIndex(3),节点C移动至index(2)的位置 |
0位置处分析:
- 从新集合中取得 B,判断老集合中存在相同节点 B,通过对比节点位置判断是否进行移动操作
- B 在老集合中的位置 B._mountIndex = 1,此时 lastIndex = 0,不满足 child._mountIndex < lastIndex 的条件,因此不对 B 进行移动操作;
- 更新 lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex),其中 prevChild._mountIndex 表示 B 在老集合中的位置,则 lastIndex = 1
- 并将 B 的位置更新为新集合中的位置prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex
- 此时新集合中 B._mountIndex = 0,nextIndex++ 进入下一个节点的判断。
1位置处分析:
- 从新集合中取得 A,判断老集合中存在相同节点 A,通过对比节点位置判断是否进行移动操作
- A 在老集合中的位置 A._mountIndex = 0,此时 lastIndex = 1,满足 child._mountIndex < lastIndex的条件,因此对 A 进行移动操作enqueueMove(this, child._mountIndex, toIndex)
- 其中 toIndex 其实就是 nextIndex,表示 A 需要移动到的位置;更新 lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex)
- lastIndex = 1,并将 A 的位置更新为新集合中的位置 prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex,此时新集合中A._mountIndex = 1,nextIndex++ 进入下一个节点的判断。
然后往后循环就行了,其终极目标就是用最少的移动来完成节点的更新
第二种有删除节点的情况
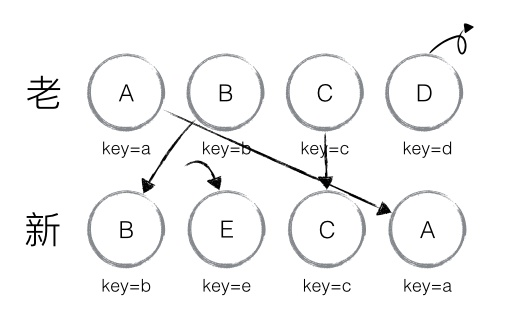
| index | 节点 | oldIndex | maxIndex | 操作 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | B | 1 | 0 | oldIndex(1)>maxIndex(0),maxIndex=oldIndex |
| 1 | E | - | 1 | oldIndex不存在,添加节点E至index(1)的位置 |
| 2 | C | 2 | 1 | 不操作 |
| 3 | A | 0 | 3 | oldIndex(0)< maxIndex(3),节点A移动至index(3)的位置 |
最后还需要对旧集合进行循环遍历,找出新集合中没有的节点,此时发现存在这样的节点D,因此删除节点D,到此 diff 操作全部完成。
- oldIndex存在
- 当oldIndex>maxIndex时,将oldIndex的值赋值给maxIndex
- 当oldIndex=maxIndex时,不操作
- 当oldIndex< maxIndex时,将当前节点移动到index的位置
- oldIndex不存在
- 新增当前节点至index的位置
加上Key值的Diff算法还是有缺陷
从末尾插入头部就会造成整层的移动,所以React官方也表明避免往头部插入数据
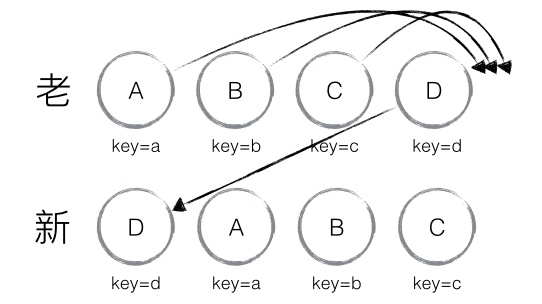
总结